Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced several key modifications to the Union Budget 2024. These developments are expected to provide a boost for personal finance among all income levels.
The goals of this budget are to lessen hardship and encourage stability. It offers adjustments to customs duties, tax slab rates, and other financial regulations. Let's see how these changes might impact your personal budget.
One of the biggest adjustments in this union budget is the increase in short term as well as long term capital gains tax. Short-term capital gains tax on specified financial assets has been hiked from 15% to 20% and Long Term Capital gains tax has been hiked from 10% to 12.5% effective July 23, 2024.
So, for Long-term capital gains, regardless of the asset type, tax will levied at a flat rate of 12.5% without indexation benefits. Also, the exemption limit for long-term capital gains in case of equity has been increased from 1 lakh to Rs. 1.25 lakh per year.
There won't be any changes to the taxation of any other assets, financial or non-financial; they will still be subject to the relevant slab rate.
The holding periods for determining Short Term or Long Term capital gains are now simplified.
Definition of Specified Mutual Fund changed to a mutual fund which invests more than 65% of its total proceeds in Debt & Money market instruments or funds which invest in such ‘specified mutual funds’.
Taxation in case of Mutual Fund categories
The budget also brings positive news for mutual fund investors. Hybrid funds, including those with significant equity exposure, gold ETFs, and international funds, will now enjoy the benefits of long-term capital gains taxation after a holding period of 24 months.
Additionally, fund of funds with over 65% exposure to domestic equity will be taxed at par with equity funds, aligning their tax treatment with equity-oriented funds.

Benefits associated with indexation for properties bought or inherited prior to 2001 will retain.
All unlisted bonds, debentures, debt mutual funds, and MLDs will be taxed at the slab rate, regardless of the holding period.
In addition, the budget proposes equalizing capital gains taxes for residents and non-residents while also making necessary changes to pertinent provisions.
The revised tax slabs under the New Tax Regime will result in a tax saving of ₹17,500:
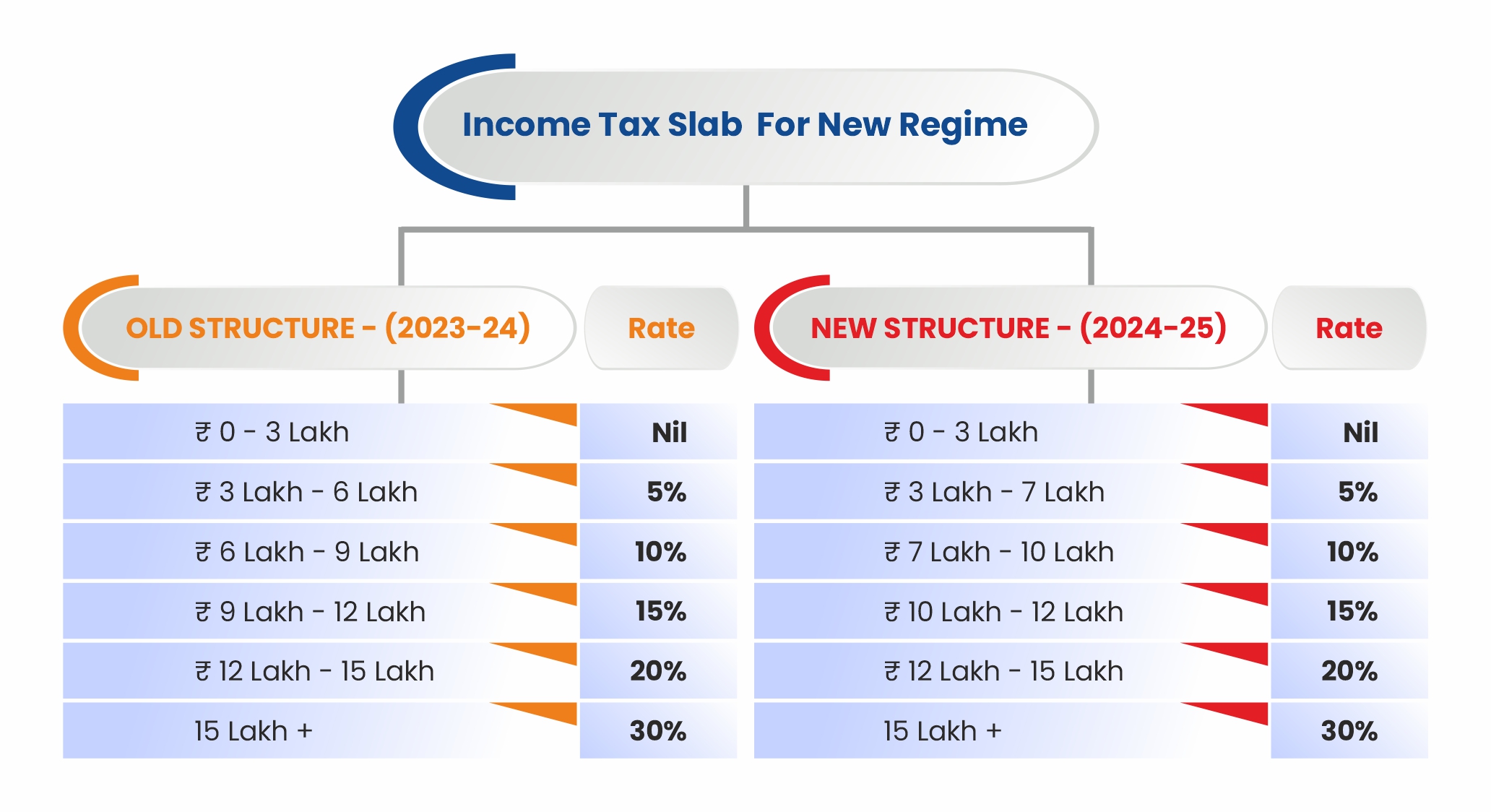
The standard deduction for salaried individuals has been enhanced from Rs. 50,000 to Rs. 75,000
The maximum amount eligible for tax deduction towards the National Pension Scheme (NPS) has been increased from 10% to 14% of basic salary for both private and public sector employees.
The deduction for family pension has been significantly increased from Rs. 15,000 to Rs. 25,000, providing substantial relief to families dependent on such income.
Employees can now inform employers of any tax at source (TCS) on luxury goods, vehicles, or foreign remittances.
From October 1, 2024, TDS will apply to interest on RBI Floating Rate Savings (Taxable) Bonds 2020 and other government securities over ₹10,000.
Finally, the TDS rates will drop from 5% to 2% for various payments. These include commissions, rent from individuals or HUF, and amounts from e-commerce operators.
Credit of all tax deducted or collected to be allowed while computing TDS on Salary
The corporate tax rate for foreign companies operating in India has been reduced from 40% to 35%.
Custom duties on gold, silver, and platinum have been decreased, and 25 critical minerals have been exempted from customs duty.
The government plans to abolish the Angel Tax, a levy on the valuation of shares issued by startups, effective from April 1, 2025.
Starting from October 1, 2024, the tax on share buybacks will shift from the company to shareholders. This means shareholders will be taxed on the amount received as a dividend income, while also being allowed to claim a capital loss for the original cost of the shares.
The Securities Transaction Tax (STT) on futures and options trading has been increased to 0.20%.
The Union Budget 2024 includes measures to improve personal finance.
The budget aims to ease financial hardship and promote stability for all. It does this through various measures, including affordable health care, customs duty changes, and tax reforms.
By using these improvements, people can better manage their money and improve their financial well-being in the coming year.